CMS156v12 – Use of High-Risk Medications in Older Adults
| Use of High-Risk Medications in Older Adults | CMS156v12 |
Percentage of patients 65 years of age and older who were ordered at least two high-risk medications from the same drug class. Three rates are reported.
3. Total rate (the sum of the two numerators divided by the denominator, deduplicating for patients in both numerators). |
|---|---|---|
| – DENOMINATOR
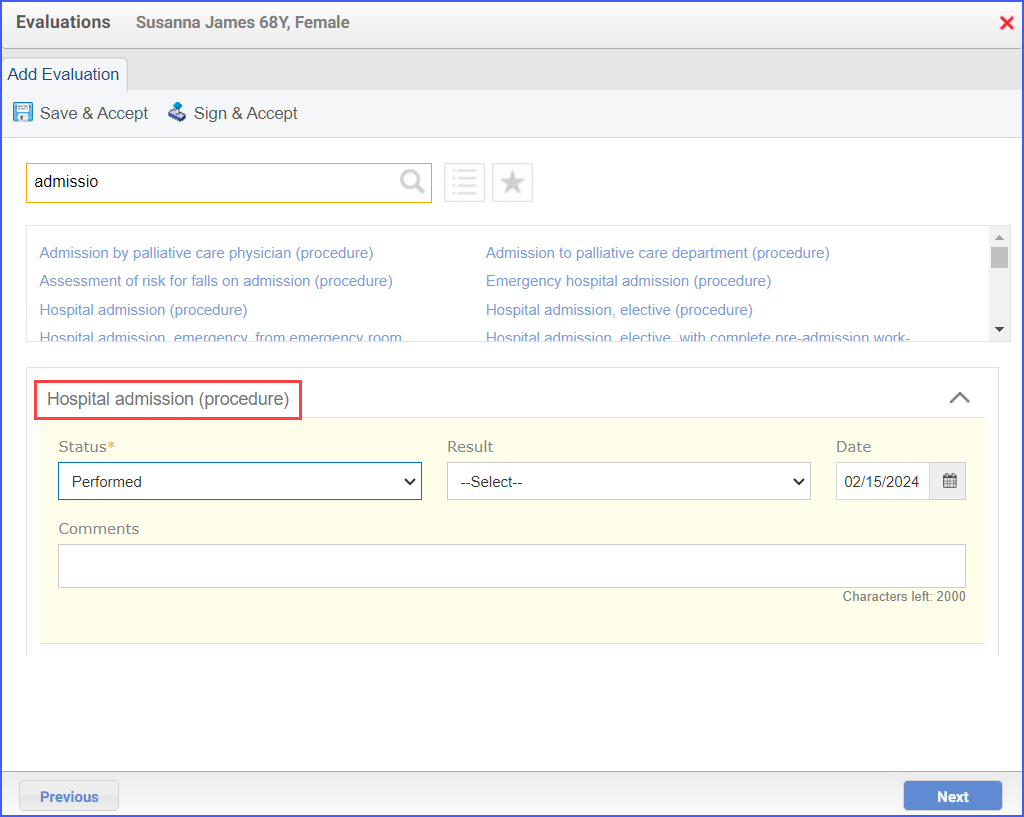
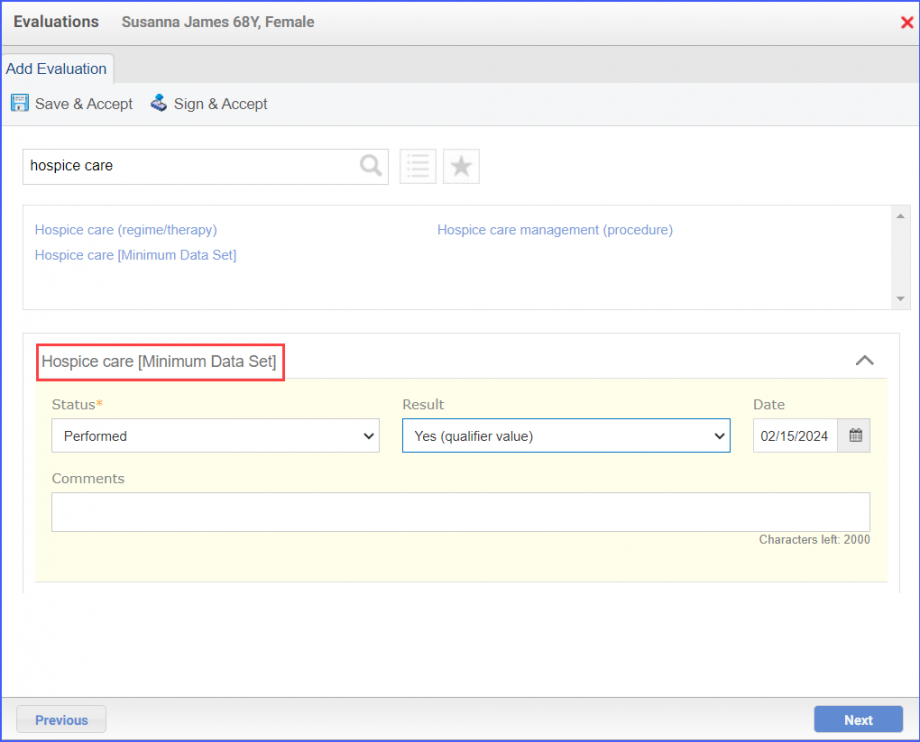
Patients 65 years and older at the end of the measurement period who had a visit during the measurement period. A qualifying visit in this case can include any of the following:
– NUMERATOR NUMERATOR 1: Patients with at least two orders of high-risk medications from the same drug class on different days. A high-risk medication is identified by any one of the following:
The following medications classify as high risk at any dose and for any duration and thus are considered for category 1a:
2. At least two orders of high-risk medications from the same drug class with summed days’ supply greater than 90 days. This medication can include prescriptions of:
owing to the fact that anti-infectives are classified as high risk at any dose with greater than a 90-day supply. Thus, it is considered for category 1b. 3. At least two orders of high-risk medications from the same drug class each exceeding average daily dose criteria. Any of the following medications are classified as high risk when they exceed the specified average daily dose, and thus are considered for category 1c:
Either of the three conditions a, b and c can be fulfilled in order to qualify for numerator 1. NUMERATOR 2: Patients with at least two orders of high-risk medications from the same drug class (i.e., antipsychotics and benzodiazepines) on different days except for appropriate diagnoses.
NUMERATOR 3: Total Rate (the sum of the two previous numerators, deduplicated). This means either Numerator 2 is true, or Numerator 1 is true but Numerator 2 is not true. – DENOMINATOR EXCLUSIONS
|
||
| – APPLICATION WORKFLOW
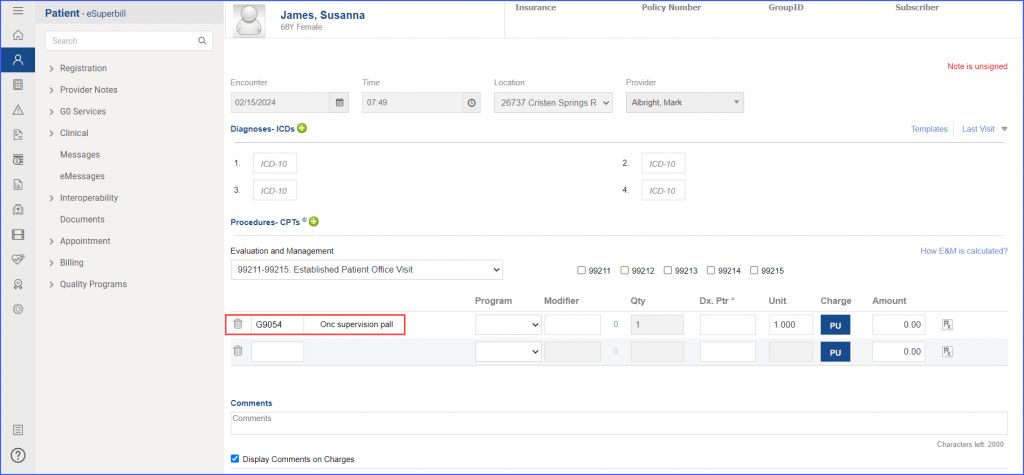
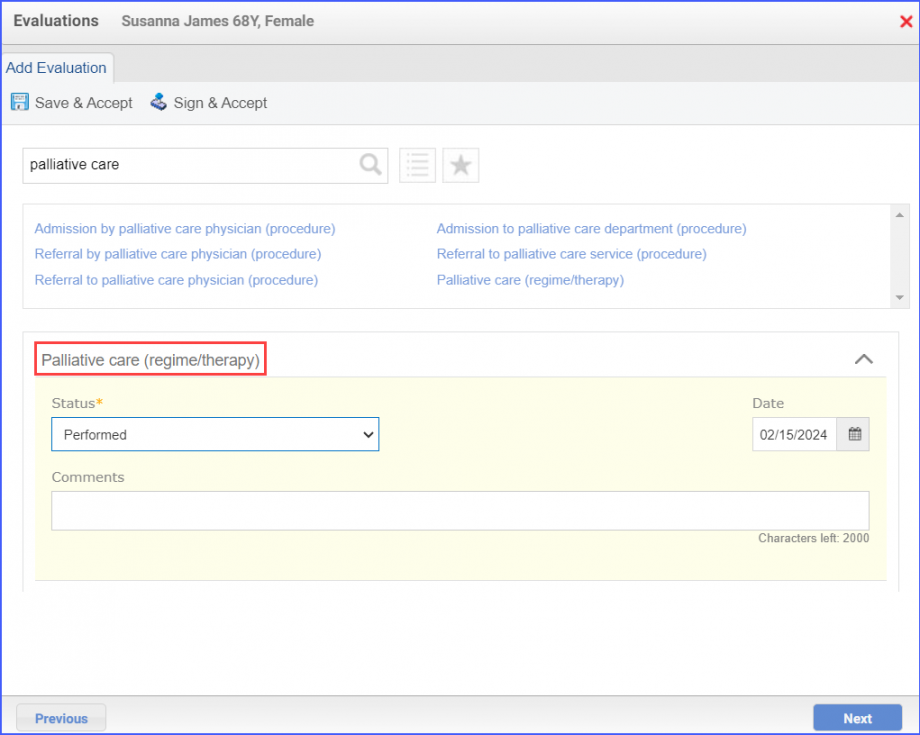
For Denominator: To record an encounter, navigate to Patient > Provider Note > Create Superbill. Under the ‘Procedure-CPTs’ heading, enter the relevant encounter code. 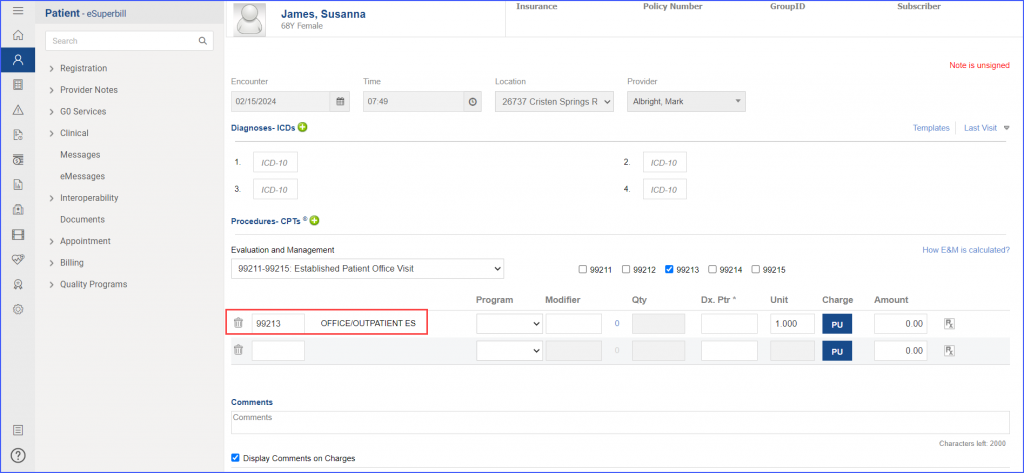 For Numerators 1 &3: To prescribe medication to a patient, navigate to Patient > Provider Note > Prescription. Click ‘Add’ and search for the relevant medication. Once done, click ‘Prescribe’. 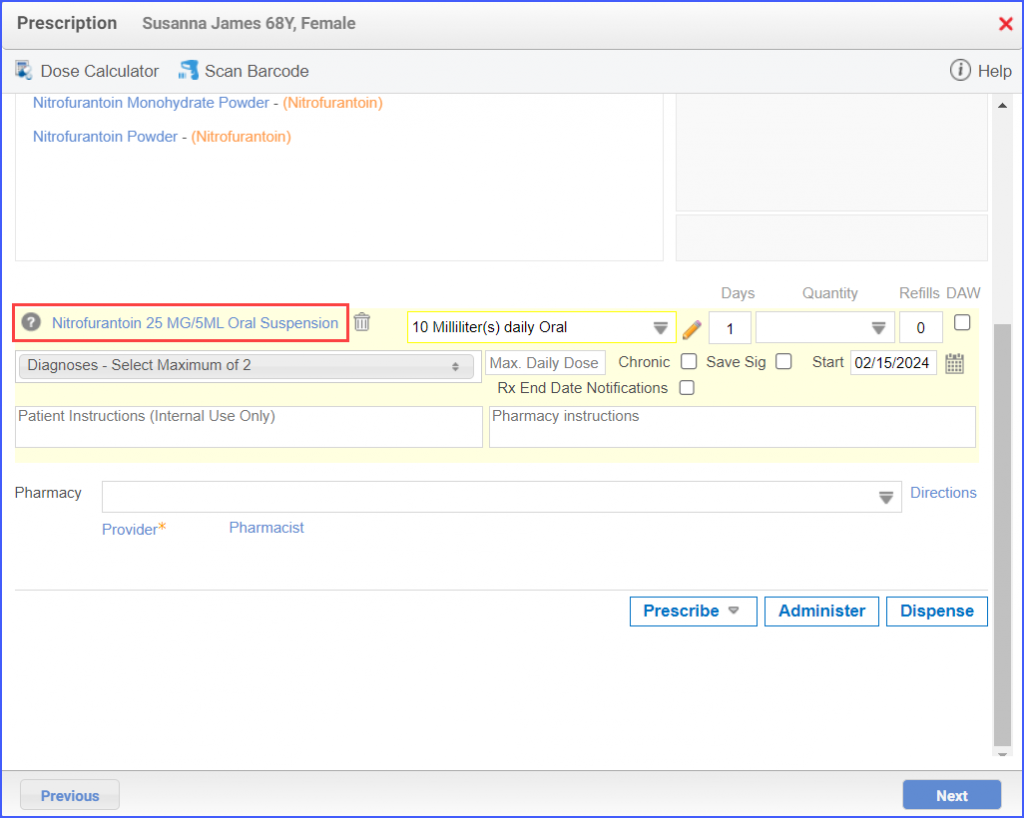 For Numerator 2: To order benzodiazepine or antipsychotics, head over to Patient > Provider Note > Prescription. Here, click ‘Add’ and search for the relevant medication, fill out the details as needed and once done, click ‘Prescribe’. 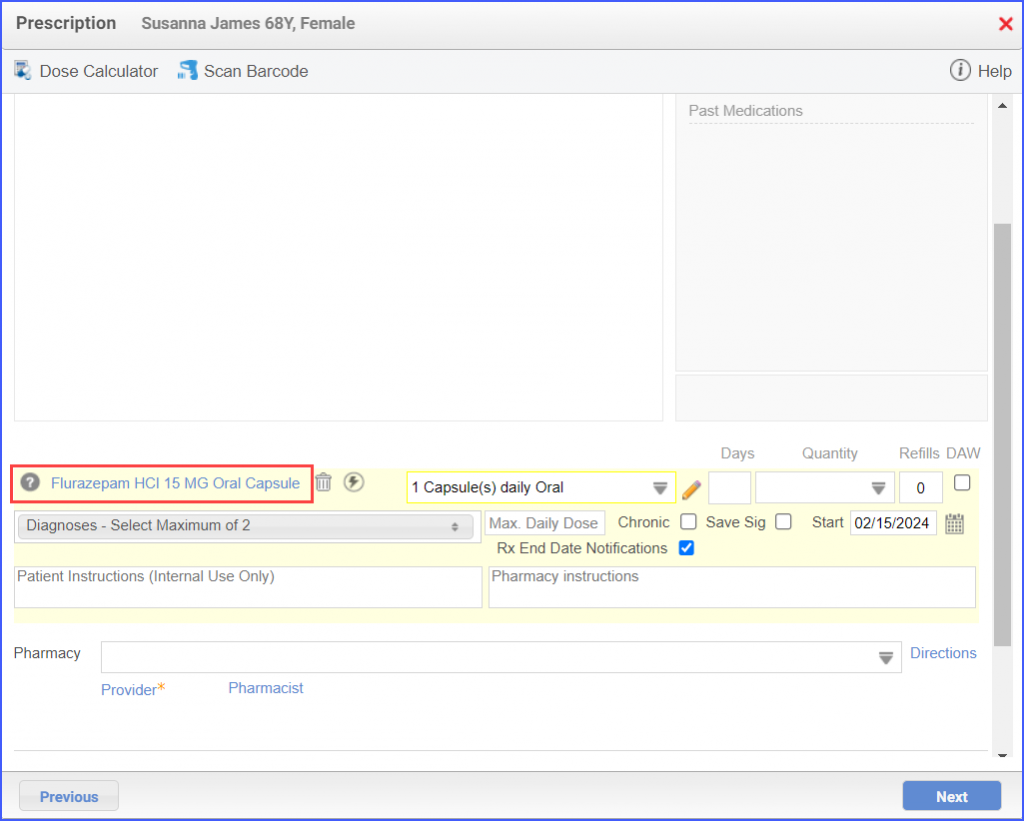 Note: It’s crucial to consider that in order to count patients in the numerator for whom antipsychotics are prescribed, they must not meet the following criteria:
Similarly, individuals who are prescribed benzodiazepines must not meet the following criteria:
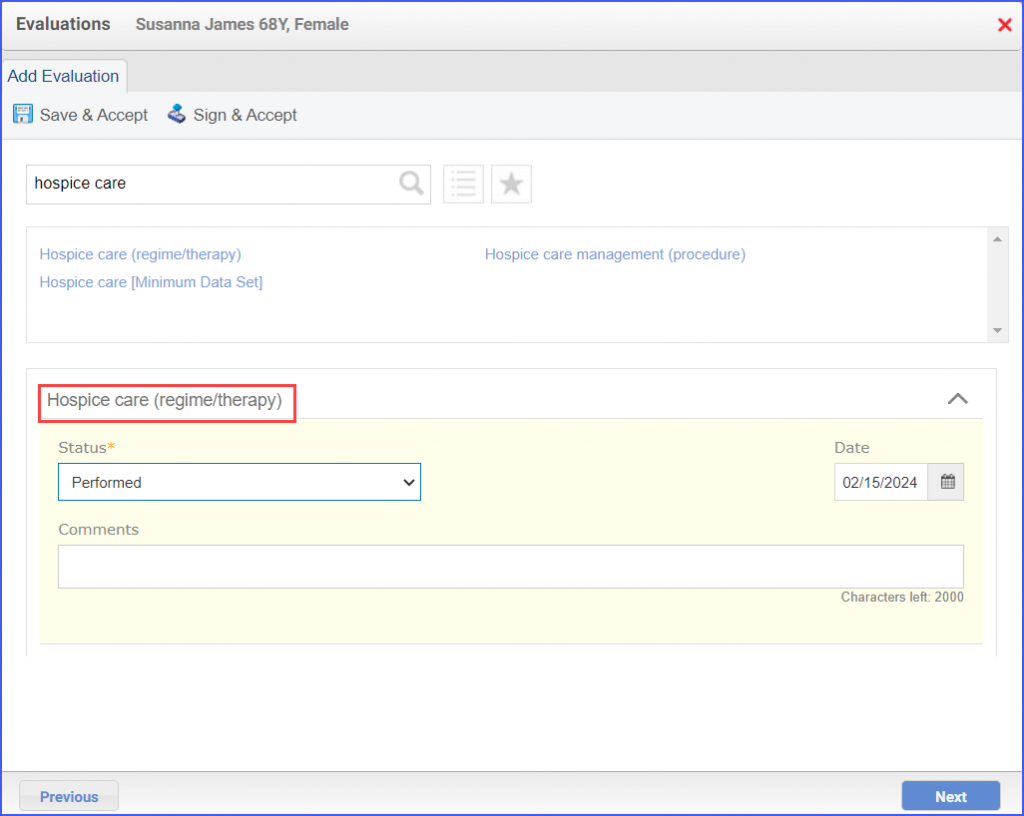
For Denominator Exclusions:
 |
||
