CMS90v13 – Functional Status Assessments for Heart Failure
| Functional Status Assessments for Heart Failure | CMS90v13 | Percentage of patients 18 years of age and older with heart failure who completed initial and follow-up patient-reported functional status assessments. |
|---|---|---|
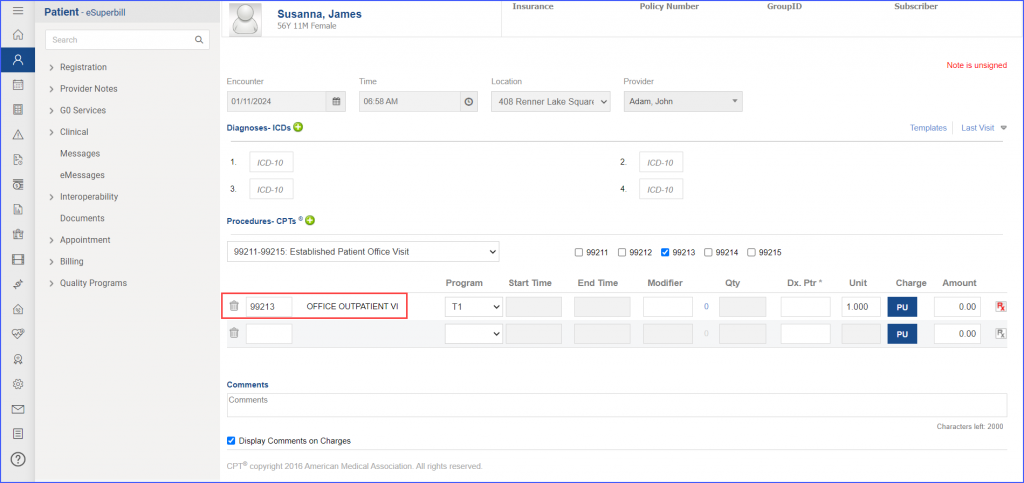
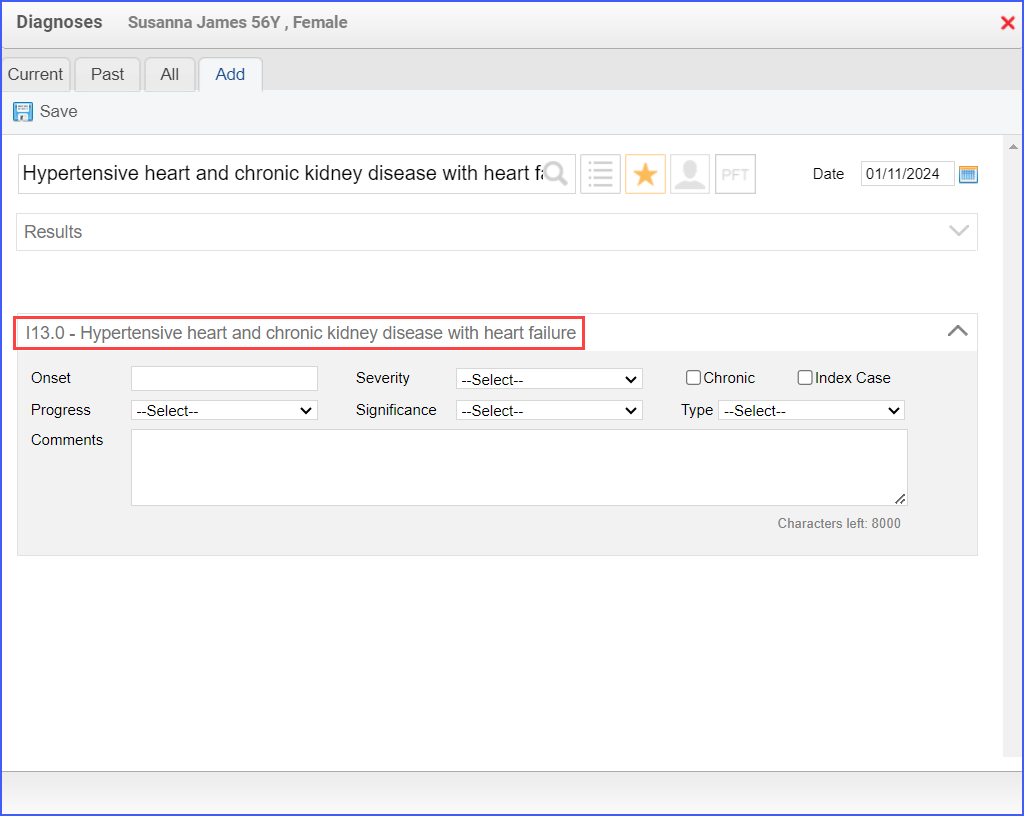
| – DENOMINATOR
Patients 18 years of age and older who had two outpatient encounters during the measurement period and a diagnosis of heart failure that starts any time before and continues into the measurement period. A qualifying outpatient encounter in this case includes:
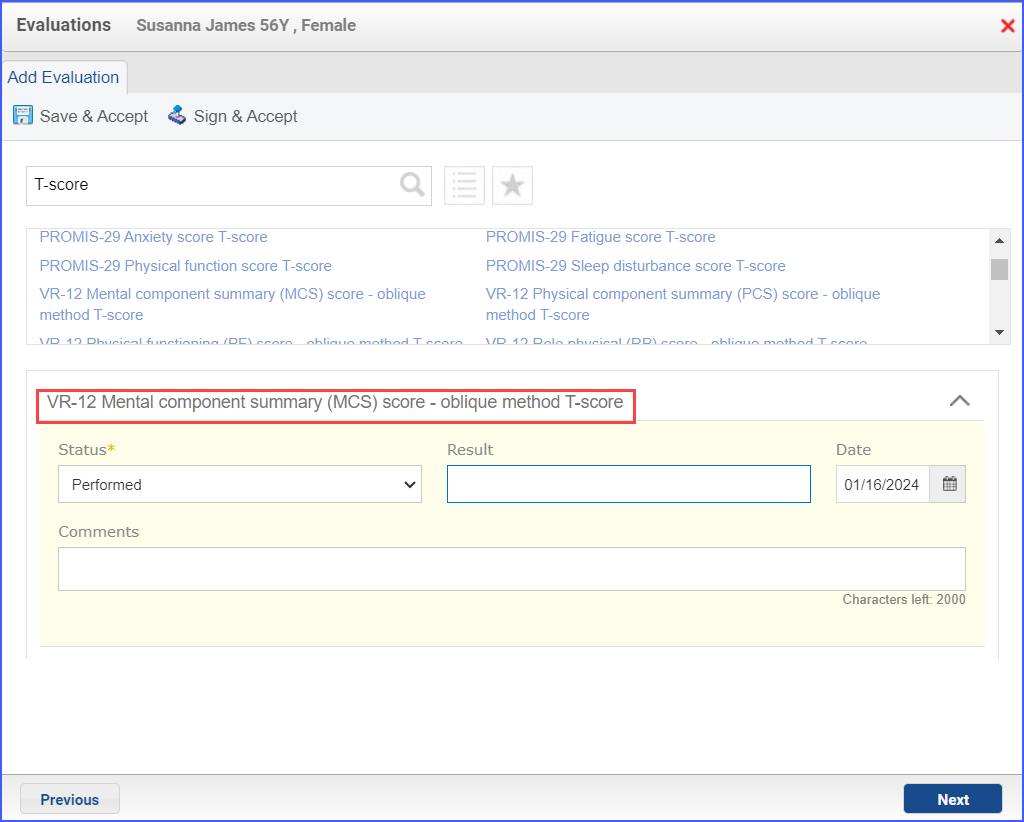
Note: The follow-up encounter should start 1 day or more after the day of end of initial visit. – NUMERATOR Patients with patient-reported functional status assessment results (i.e., Veterans RAND 12-item health survey [VR-12]; VR-36; Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire [KCCQ]; KCCQ-12; Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire [MLHFQ]; Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System [PROMIS]-10 Global Health, PROMIS-29) present in the EHR within two weeks before or during the initial FSA encounter and results for the follow-up FSA at least 30 days but no more than 180 days after the initial FSA. The functional status assessments can include any of the following:
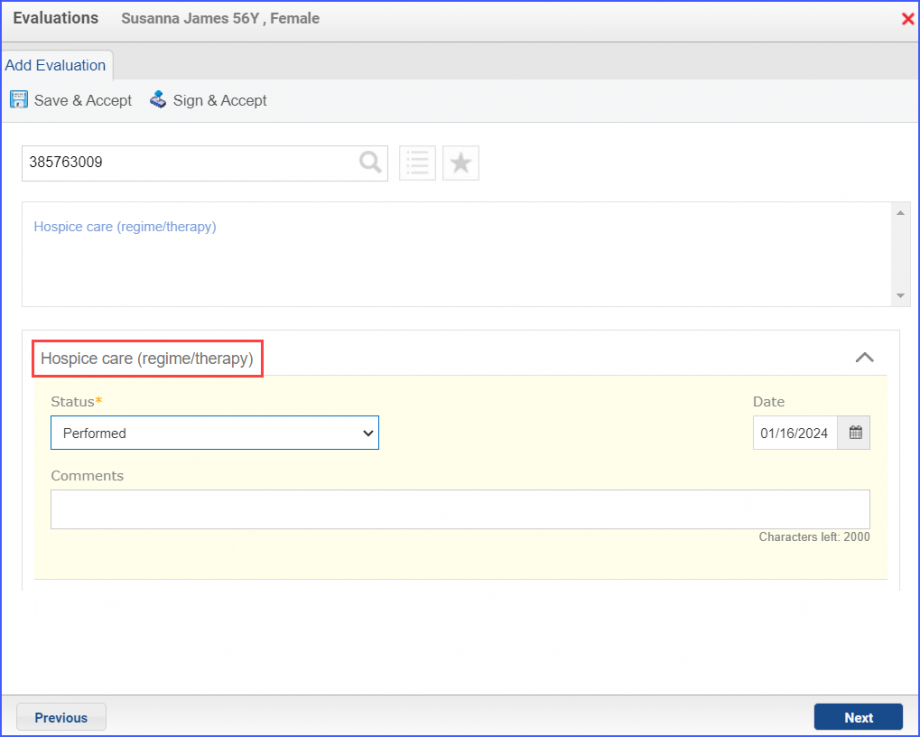
– DENOMINATOR EXCLUSIONS
|
||
| – APPLICATION WORKFLOW
For Denominator:
 For Numerator:
 Note: The result for an assessment must not be null and all the assessments pertaining to a specific assessment category must be recorded on the same day. For Denominator Exclusions:
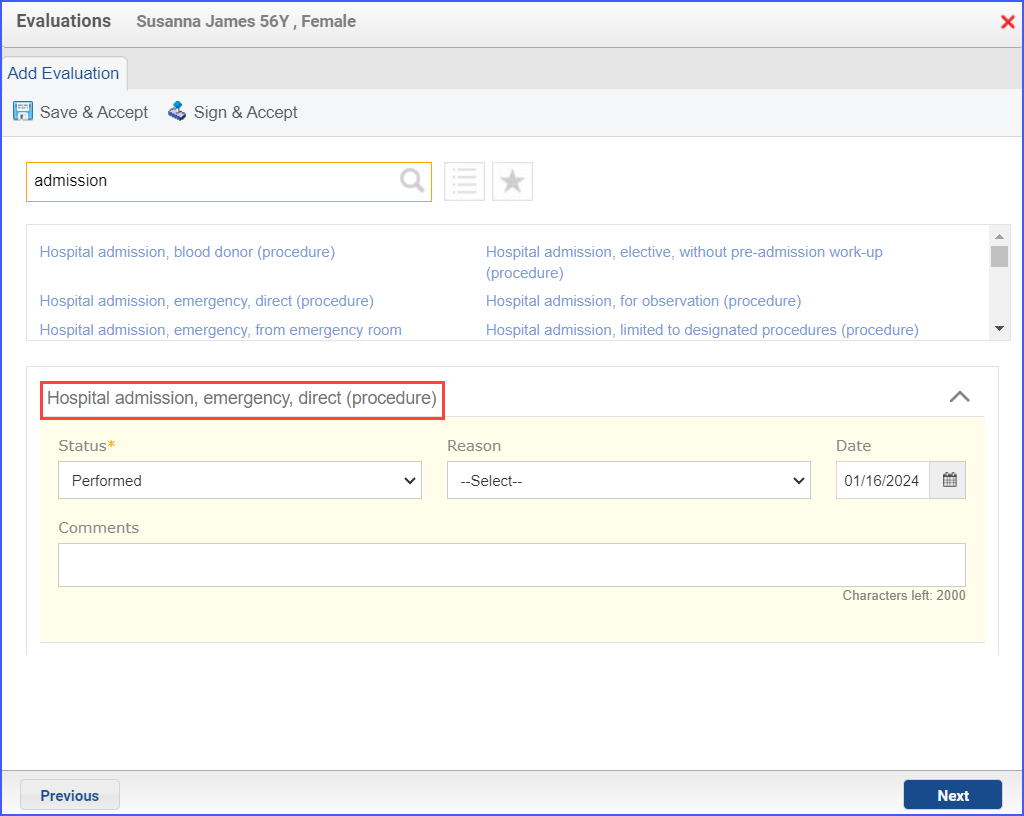
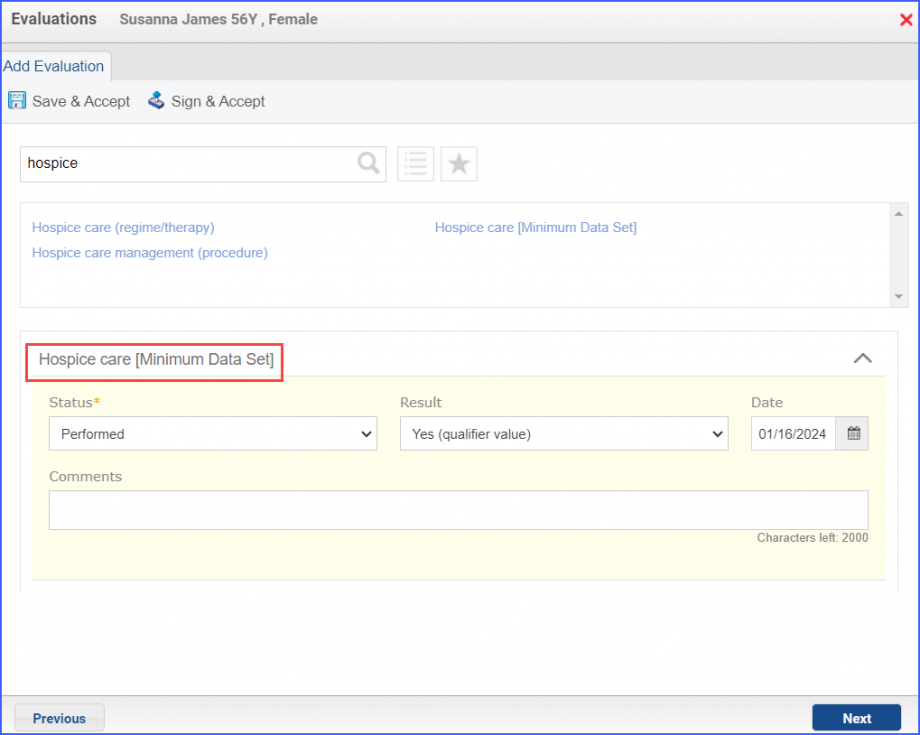
|
||
