CMS771v4 – Urinary Symptom Score Change 6-12 Months After Diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
| Urinary Symptom Score Change 6-12 Months After Diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia | CMS771v4 | Percentage of patients with an office visit within the measurement period and with a new diagnosis of clinically significant Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia who have International Prostate Symptoms Score (IPSS) or American Urological Association (AUA) Symptom Index (SI) documented at time of diagnosis and again 6-12 months later with an improvement of 3 points |
|---|---|---|
| – DENOMINATOR
Male patients with an initial diagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BHP) 6 months prior to, or during the measurement period, and a urinary symptom score assessment (IPSS or AUASI) within 1 month of initial diagnosis and a follow-up urinary symptom score assessment within 6-12 months, who had a qualifying visit during the measurement period. A qualifying visit in this case is an Office Visit. Note: With the American Urological Association Symptom Index [AUASI], a quality of life assessment ‘If you were to spend the rest of your life with your urinary condition just the way it is now, how would you feel about that [IPSS]’ is to be performed as well. – NUMERATOR Patients with a documented improvement of at least 3 points in their urinary symptom score during the measurement period.. – DENOMINATOR EXCLUSIONS
For hospitalization, an encounter for ‘Hospital Services for urology care’ must exist.
|
||
| – APPLICATION WORKFLOW
For Denominator:
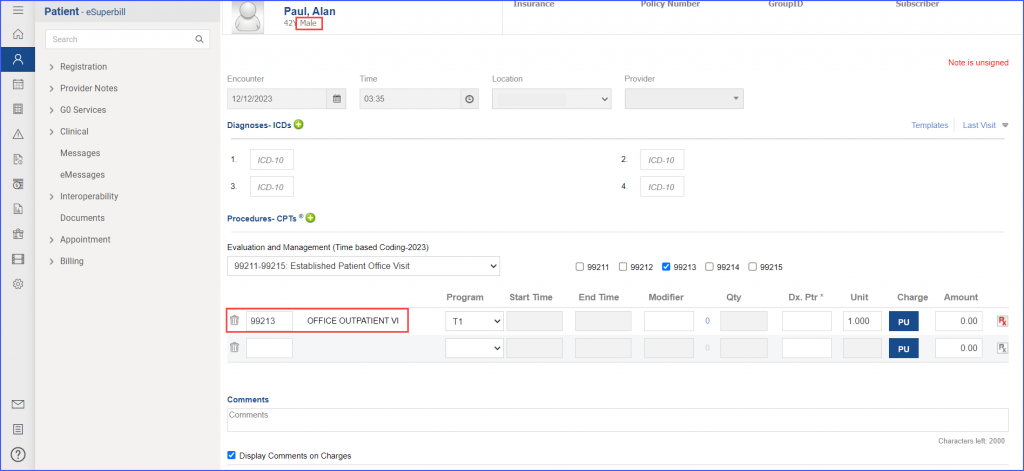
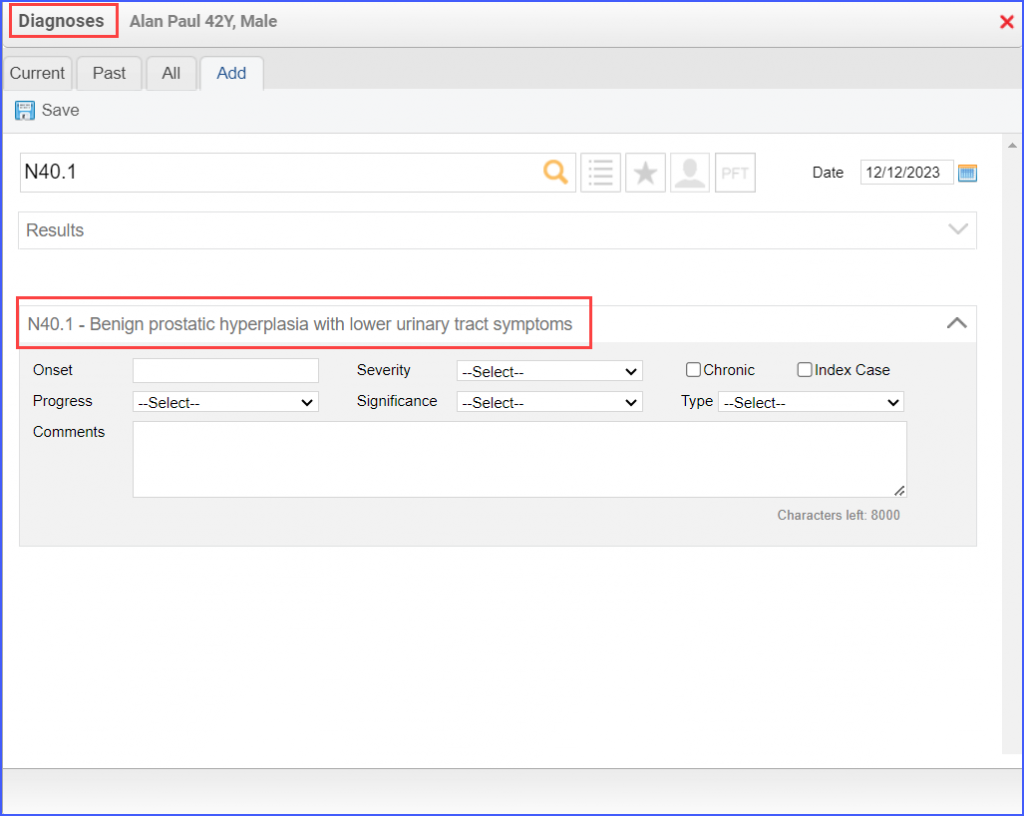
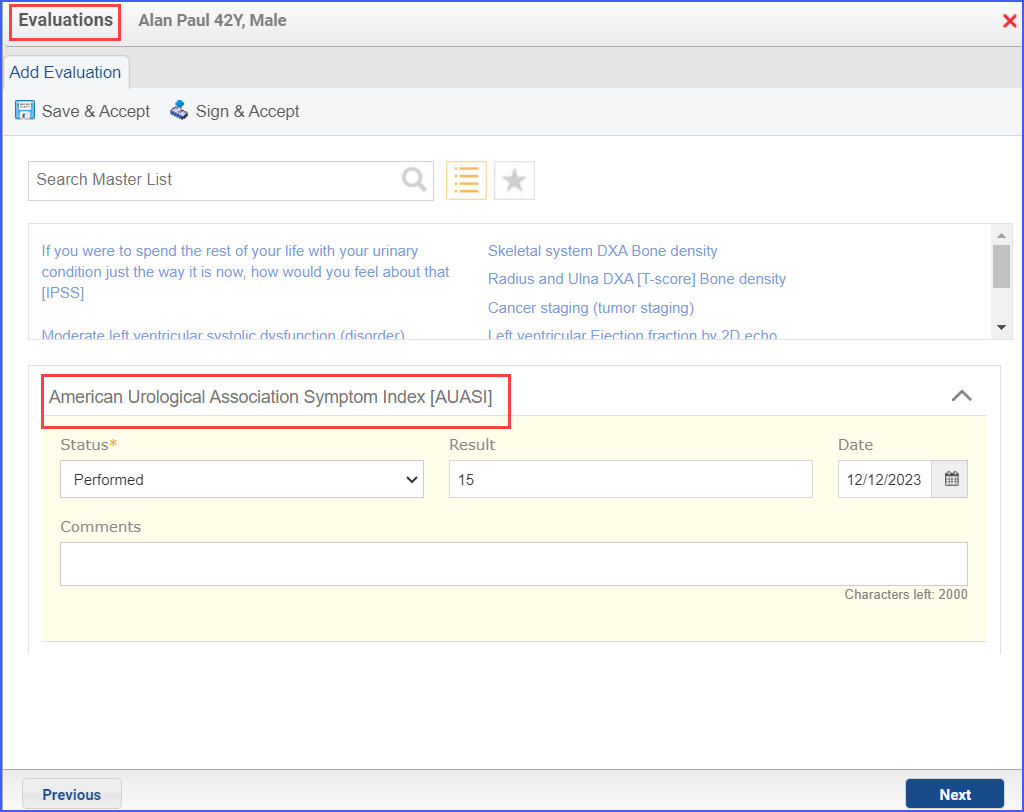
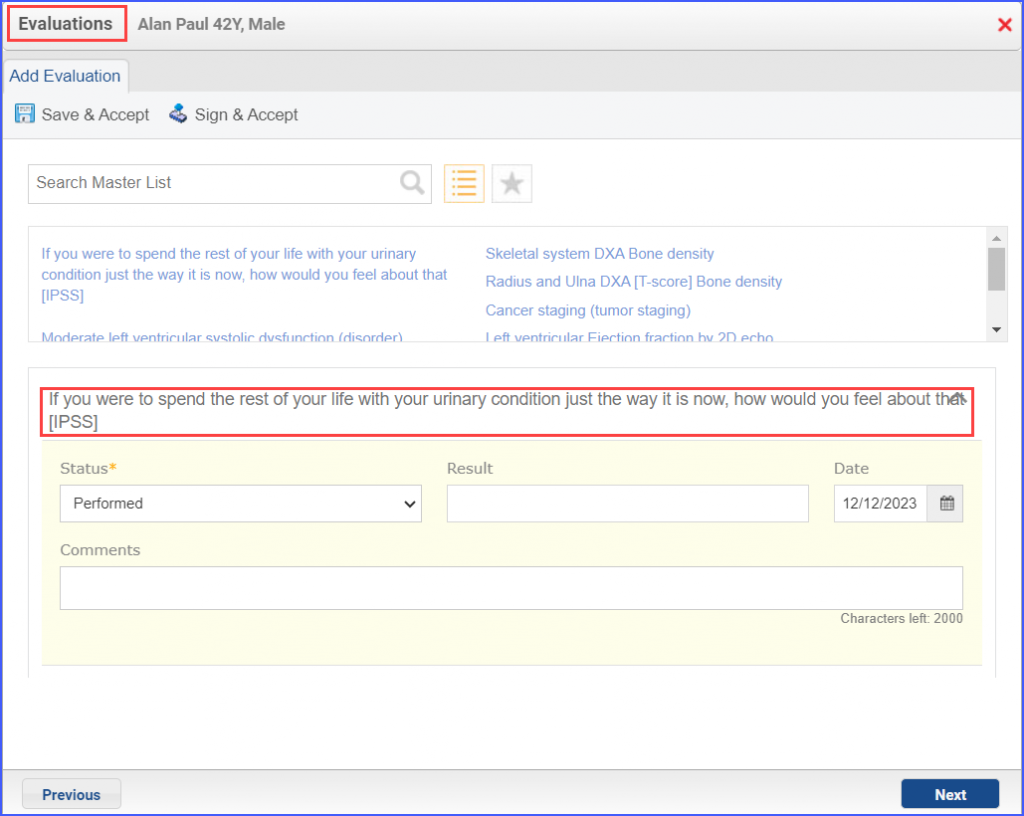 For Numerator: The urinary symptom score change (including the quality of life assessment) can be documented as guided in the Denominator workflow. Note: In order to be counted in the numerator, the BPH diagnosis must exist for a patient (which can be documented as mentioned in the denominator workflow). For Denominator Exclusions:
use the workflow Patient > Provider Notes > Diagnoses. Here, click ‘Add’ and search for the relevant diagnosis. Fill out the details if needed and once done, click ‘Save’. 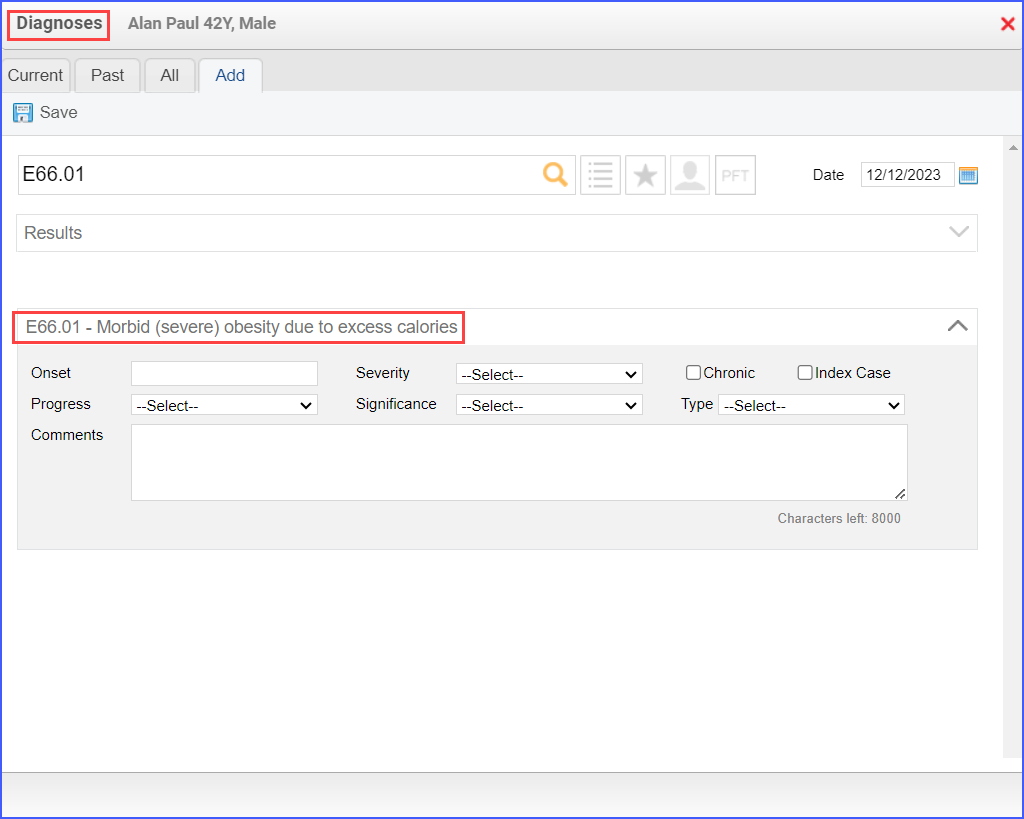
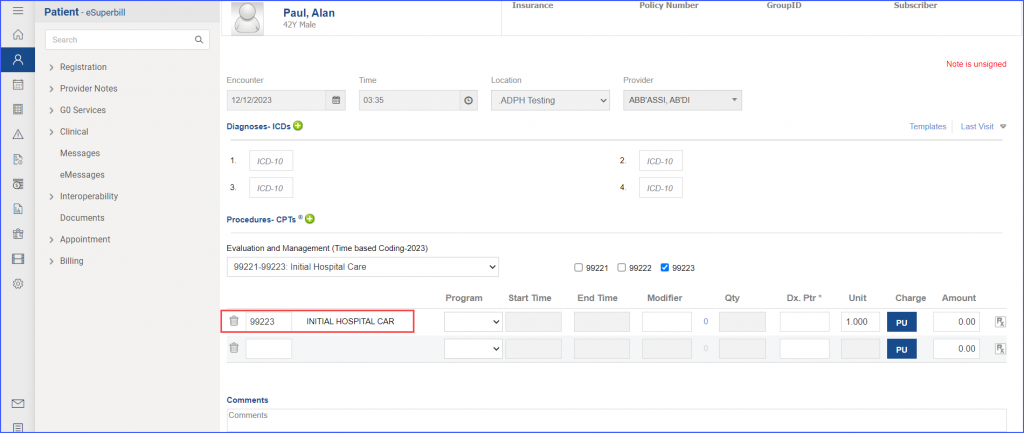
|
||